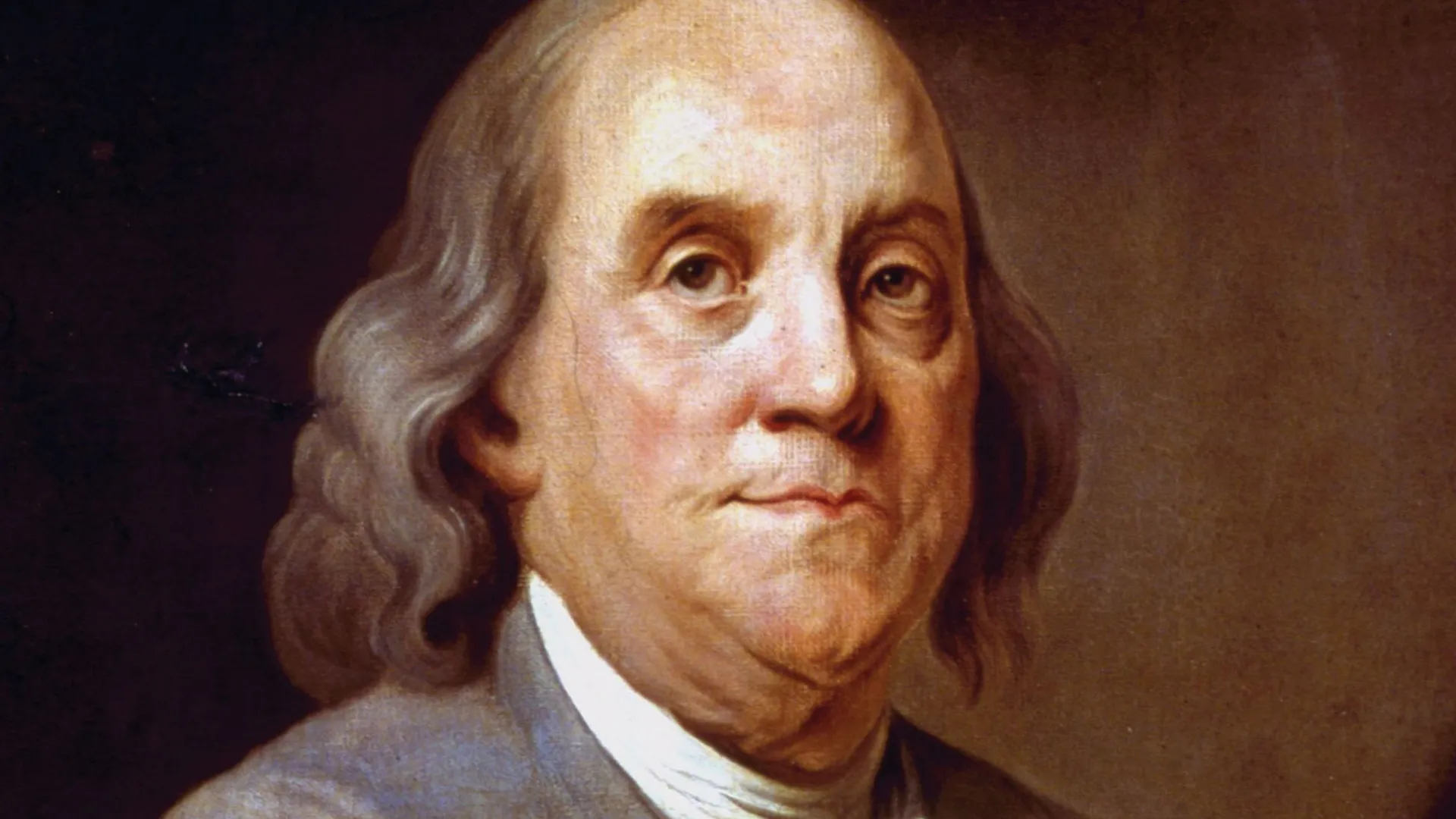
The role of the national diplomat is very significant in any democratic government. It plays an imperative role in building communication with other countries. In this inclusive article, we are writing about Benjamin Franklin, who was a brilliant ambassador who has proved his mastermind all over the world. Benjamin Franklin was born in Boston, Massachusetts, on January 17, 1706, and he was a fount of knowledge, statesman, scientist, inventor, and one of the Founding Fathers of the United States.
Franklin multi-layered help spanned the territories of science, literature, politics, and diplomacy, leaving an unforgettable mark on US history. This article probes into the unique life of Benjamin Franklin, studying his successes, education, personal life, and permanent legacy.
Benjamin Franklin Early Life And Education:
Franklin was the 15th of 17 children in a modest family. His formal education finished when he was almost ten years old, due to family circumstances he started working in his father’s candle and soap-making business. In spite of that, Franklin’s voracious interest and love for reading led him to teach himself through insatiable reading and self-study. Benjamin autodidactic searches laid the foundation for the academic giant Franklin would become.
Benjamin Franklin Personal Life:
Franklin’s personal life was marked by a promise to self-improvement and virtue. His “Biography” summaries his thirteen virtues, such as industry, stinginess, and humbleness, which he intended to promote throughout his life. Franklin’s common-law marriage to Deborah Read produced two children, and Benjamin also had an illegitimate son, William, who played an important role in foreign politics.
Franklin Career as a Printer:
At the age of seventeen, Benjamin Franklin left Boston for Philadelphia, where he improved his skills as a printer. In the year 1729, he bought The Pennsylvania Gazette, a newspaper that he transformed into one of the most powerful publications in the American colonies. Franklin’s journalistic prowess and humorous writing style made him a well-known figure, resting the groundwork for his future political career.
Franklin Scientific Contributions:
Franklin’s inquisitiveness extended to the natural world, and he made revolutionary contributions to science. Franklin research with electricity, including the famed kite experiment in 1752, established the idea of positive and negative electrical charges. Franklin’s work on the discovery of the lightning rod established his practical application of scientific knowledge for the improvement of society.
Franklin Inventions and Innovations:
Franklin’s resourceful mind led to several practical innovations. He created the Franklin stove, an efficient heating appliance that transformed home heating. His spectacles, still in use today, mutual lenses for myopia and farsightedness in a single pair of glasses. Moreover, Franklin is credited with emerging the odometer, a device for calculating distances traveled.
Franklin Political Career:
Benjamin Franklin’s political career started in earnest in the 1750s. Franklin work for as a colonial agent, on behalf of Pennsylvania and other colonies in United Kingdom. Franklin diplomatic skills became obvious during the Albany Congress of 1754, where he planned the Albany Plan of Union, a forerunner to the later American Union. Benjamin’s participation in the drafting of the Declaration of Independence and the United States Constitution hardened his status as a key figure in the nation’s founding.
Diplomacy and International Relations:
Franklin’s diplomatic acumen was vital during the American Revolution. He played an essential role in securing French support for the American cause & negotiating the Treaty of Alliance with France in 1778. Franklin’s diplomatic hard work continued with the Treaty of Paris in 1783, which over the Revolutionary War and established the United States as a sovereign nation.
Franklin Legacy:
Benjamin Franklin passed away on 17th April, 1790, in Philadelphia. Franklin legacy endures as a symbol of American inventiveness, intellectual curiosity, and civic responsibility. Franklin’s contributions to science, politics, and literature formed the foundation of the United States and continue to motivate generations.
Summary:
Benjamin Franklin’s life was an evidence to the unlimited potential of the human mind. His voyage from a humble learner to a revered Founding Father imitates the essence of the American Dream. Franklin’s lasting legacy extends out there his palpable inventions and political attainments; it lies in his commitment to incessant learning, civic duty, and the chase of knowledge for the benefit of society. Source: WikiPedia